Learn everything you need to know about VESA Display Stream Compression (DSC), simply explained in our blog. Start reading!
Display technology has advanced in leaps and bounds over the past decade. Electronics manufacturers have been using increasingly sophisticated display features as a way of differentiating their products in the highly competitive consumer electronics market. Each new generation of products pushes the boundaries of display technology even further and this is where VESA® DSC comes in!
Industry Landscape: Why is VESA DSC needed?
VESA DSC is needed to handle the sheer amount of pixel data required for displays with higher resolutions, faster refresh rates, and increased pixel depth.
Whether it is a mobile, augmented- and virtual reality (AR/VR), or automotive display, an application processor (AP) generates pixel data, which is then transported over a physical interface (PHY) to the display. As display resolutions have increased, so has the amount of pixel data transferred over the PHY. This leaves designers with the tough task of finding ways to transport all this data over current display interfaces, without compromising on cost, power consumption, and, most importantly, visual quality.
Between 2010 and 2020, display resolution in mobile phones went from HD (1280×720) to 4K (3840×2160) with frame rates doubling and pixel depth increasing from 24 to 30 bits per pixel. This represents a growth of 23X in display bandwidth requirements from second (Gbps) to 29.9 Gbps! Across the mobile, AR/VR, and automotive markets, display bandwidth usage has been growing by approximately 40% per year, while the bandwidth of the available display physical (PHY) interfaces has increased at half that rate.
There are few ways to close this gap between the two; designers can either increase the number of physical data lanes in their design, which in turn has a knock-on effect on cost, power consumption and electromagnetic interference (EMI), or they can use video compression to reduce the total bandwidth requirements.
What is VESA display stream compression?
VESA display stream compression is a visually lossless compression standard developed by the Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA).
VESA recognized the need for video compression on display interfaces and first initiated efforts for a common, industry-wide standard in 2012. What followed in 2014 was the release of VESA Display Stream Compression (DSC), the industry’s first visually lossless video compression standard.
DSC can compress any image to 8 bits per pixel (bpp), which results in a 3X compression ratio for a 24 bpp image or a 3.75X compression ratio for a 30 bpp image.
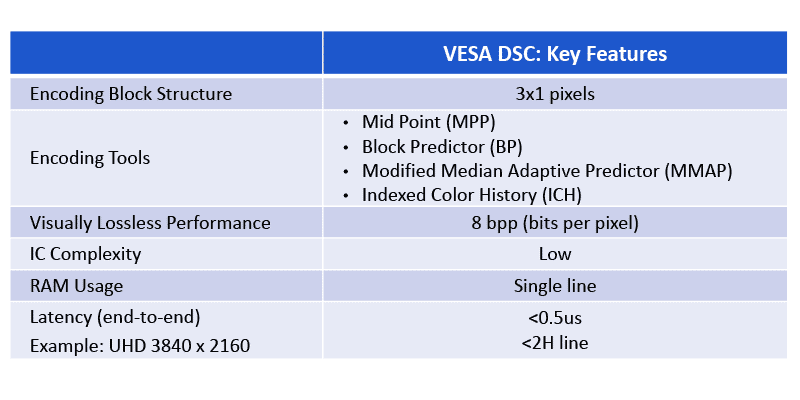
Key Features of VESA DSC
Which display interface standards have adopted DSC?
VESA DSC has been adopted by the major display interface standards for use in both embedded and external displays.
MIPI® Alliance was the first organization to adopt the use of DSC inside its interface standard, MIPI Display Serial Interface (DSISM). DisplayPort™ (DP) 1.4, released in 2016, was then the first display interface standard for external displays to adopt DSC. The HDMI® Forum followed suit in 2017 and adopted DSC in the HDMI 2.1 standard.
As of today, DSC is now also specified in the latest versions of DisplayPort, DP 2.0 and 2.1, Embedded DisplayPort (eDP) 1.4 and 1.5, as well as MIPI DSI-2.
What applications use VESA DSC? What are the benefits of using video compression?
While initially designed for mobile devices, VESA DSC has been widely adopted for use in other display-based products including AR/VR headsets, cars, TVs, computer monitors, and GPUs (graphic processor units).
Trends across several industries have driven the need for and subsequent widespread adoption of VESA DSC.
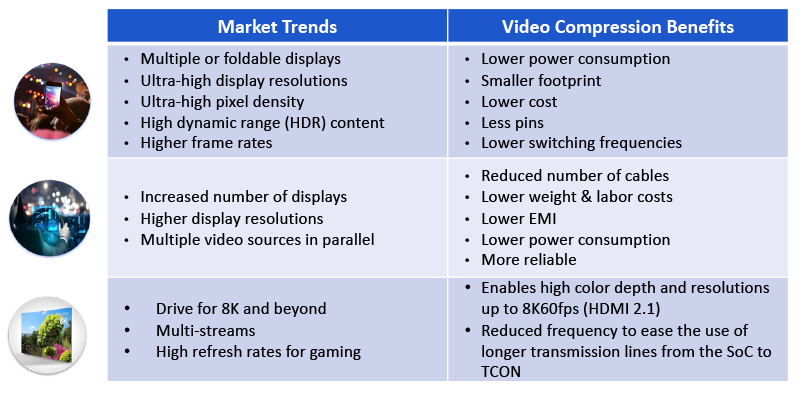
Market trends and video compression benefits
Display stream compression works by reducing (through compression) the total amount of bandwidth required for an application.
By applying video compression in your design, you can typically cut the number of transport lanes in half, which translates to many benefits, including lowering power consumption, EMI, and reducing overall costs.
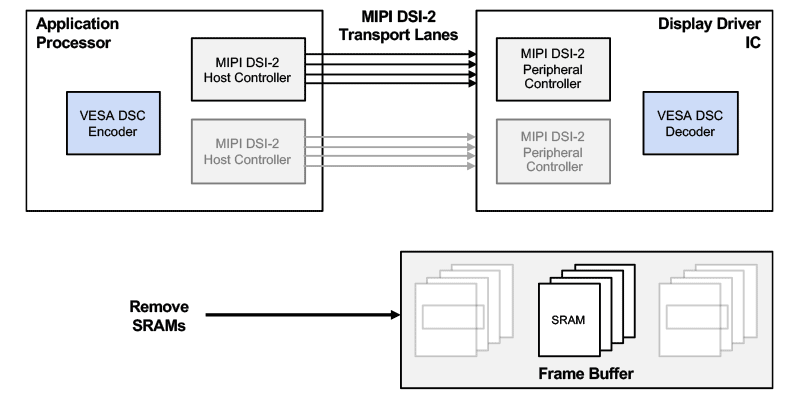
Example of VESA DSC used with the MIPI DSI-2 interface
Is Display Stream Compression (DSC) noticeable?
No, images compressed with DSC cannot be visually distinguished by users from the uncompressed versions.
People often ask this question, as well as: “does display stream compression affect image quality?.” The short answer is, no! VESA DSC is a visually lossless compression algorithm. This means that when used, no perceptible difference can be detected by the human eye. VESA rigorously tested the algorithm before it was released using a standardized methodology for subjective testing. Users were shown all types of content including natural and test images, text, graphics, etc., and the results showed that DSC is visually lossless for all types of content down to 8 bpp. Test images and a summary of test results are available from VESA.
What about DSC latency?
DSC is an extremely low latency compression algorithm.
The fact that DSC has low latency is an extremely important design characteristic, especially in the automotive and AR/VR industries.
Keeping latency low for AR/VR applications is extremely important as it avoids potential motion sickness associated with the brain detecting small delays between the body’s physical movement and the image in the head-mounted device. And for automotive applications, low latency is extremely important for safety-critical displays in cars where it is vital that there is no delay between what is being captured by a camera and what the driver sees inside the car.
Rambus VESA DSC IP Solutions
Originally developed by Hardent, Rambus offers VESA DSC encoder and decoder IP cores for both ASIC and FPGA designs.
These IP cores are silicon proven, and with 100+ design wins they offer a mature IP solution to speed up the product development cycle and lower design risk.
Past customers include major AP (application processor) and DDIC (Display Driver Integrated Circuit) vendors, as well as leading automotive, AR/VR, and test equipment manufacturers. Read how Kinetic-IC selected Hardent’s VESA DSC IP cores to create ultra-low power Multi-Stream Transport (MST) hub with VESA DSC support.
Rambus also partners with top-tier MIPI C/D-PHY suppliers, such as Mixel and Samsung, to offer display subsystem solutions comprising of the Rambus MIPI DSI-2 Controller, the Rambus (formally Hardent) VESA DSC Encoder, and the Mixel or Samsung C/D PHY. These solutions enable designers to lower project risk and accelerate time-to-market with a fully integrated display subsystem solution.
Final Thoughts
VESA DSC is a proven, visually lossless compression algorithm that helps designers meet their next-generation product design goals.
Video compression is essential for meeting the bandwidth requirements of current and future display applications. Integrating video compression into a design and achieving desired display features can be complex. Rambus VESA DSC IP and IP subsystem solutions are available to help designers lower risk and achieve faster integration when creating next-generation display products.
Additional Resources
- Rambus VESA DSC Video Compression IP Cores
- Whitepaper | MIPI Drives Performance for Next-Generation Displays
- Webinar | Next-Generation Displays: An Integrated IP Solution from Mixel, Rambus & Hardent

Leave a Reply